
Skip to the Relevant Section
Metadata is information in the HTML of a web page that is read by search engines and web crawlers. Nearly all metadata is invisible to visitors.
Search engines like Google use metadata to interpret additional information about web pages.
Search engines use the information contained in SEO metadata to:
Better understand and contextualise web page content
Display information about the page in SERPs
Display rich featured snippets
Ensure that your site is easy to navigate
Understand which parts of your website are important and which to overlook
Metadata is key because it tells search engines what a web page is about. They are like the first impression search engines get of web pages – much like an “instruction manual” on how to read the page or site.
Metadata is a crucial element to SEO because it can affect the way that your pages are displayed in search results, which can determine whether or not users click through to your site. Since click-through rate (CTR) is a ranking factor, metadata plays an important role in SEO.
Metadata also plays a role in matching your web pages to search intent. Search engines increasingly value a good user experience. That includes making sure that your site satisfies a user’s query.
By accurately matching your title tags and meta descriptions to your pages’ content, you can ensure that what users see in SERPs, is what they’ll get on your pages. This will decrease bounce rates.
This is why it’s so important to optimise your SEO metadata effectively. Want to know how your website is measuring up? Get a free SEO Audit Report.
There are numerous types of meta tags, all of which have different roles. Not all of them are relevant to search engine optimisation.
For the purposes of this quick guide, we’ve picked out seven of the most important meta tags that are relevant for SEO and search experience optimisation (SXO).
1. Title Tag
The title tag appears on SERPs and in browser tabs. The purpose of the title tag is – as the name suggests – to specify the page title. Because the page title is the first information about a page a user sees, it’s important that the title tag encapsulates the topic of the page accurately. This plays a determining factor in whether the user clicks through to the page or not. 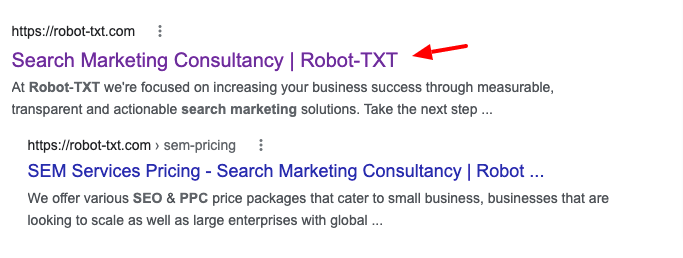
2. Meta Description
The meta description sums up the content of your web page. Search engines show the meta description in SERPs below the title tag.
It’s best practice to include your focus keyword in the meta description. Including the keyword in the meta description is a relevancy signal for search engines, which can help improve rankings.
Meta descriptions can also impact CTR, which is a key ranking factor. So it’s important that the meta description provides an accurate, enticing summary of the page content.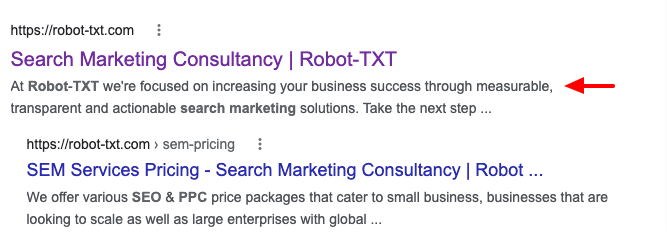
3. Alt Text
Images form a crucial part of many web pages. However, search engine can’t “see” images. Alt text (or the alternative text tag) is a way around that issue. It describes images to search engines so they know how to interpret them and rank them for relevant image search queries. 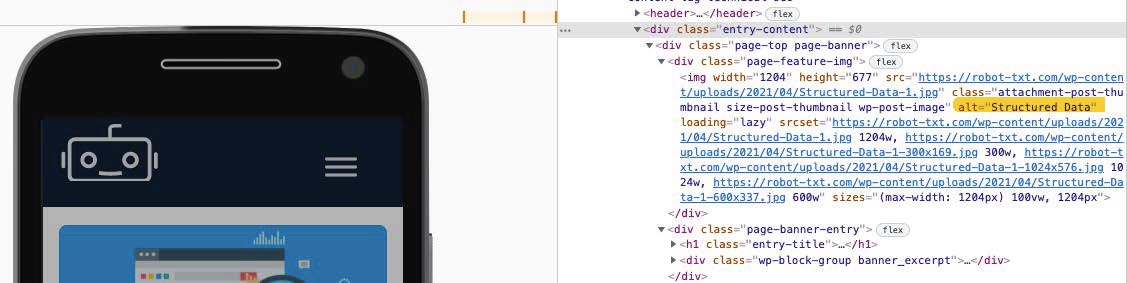
4. Header Tag
Header tags indicate the level of hierarchy of information on the page, with H1 being the most important, main heading and H6 being the least important. 
5. Responsive Design Tag
The responsive design meta tag (also called the viewport meta element) allows web designers to configure how a page scales according to device. The below example demonstrates how the content on the page adapts and scales according to screen size.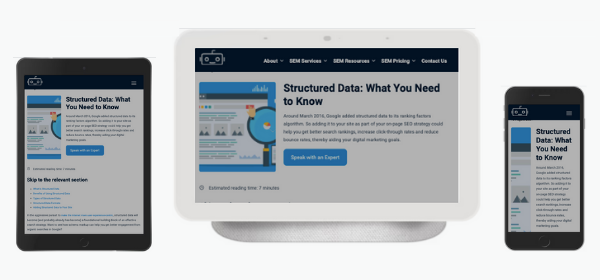
6. Canonical Tag
A canonical tag is used when there are several versions of the same web page. By implementing the canonical tag in a page’s code, your website tells search engines that this URL is the main page and that the other pages shouldn’t be indexed. This way, you can prevent problems caused by identical or “duplicate” content appearing on multiple URLs.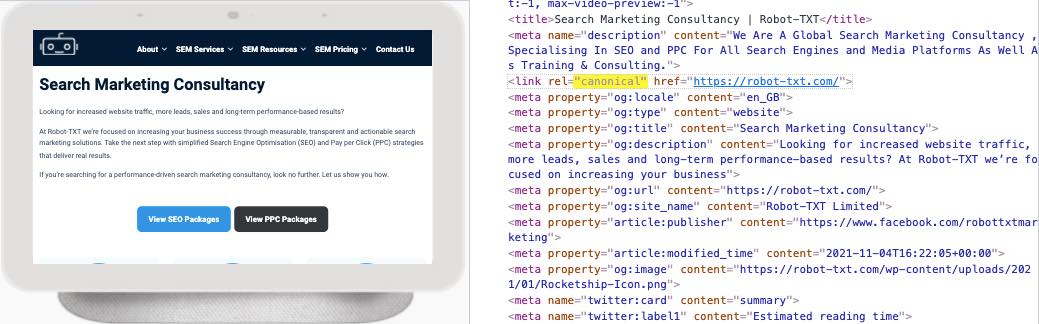
7. Robots Tag
The robots meta tag is placed in the <head> section of your page. The robots tag lets search engines know which pages on your site should be indexed.
Robots tags could be useful when you have some pages on your site that are necessary, but with quite thin content. In this instance, you can use a “noindex” tag to prevent them from appearing in the SERPs.
The robots meta tag serves a similar purpose to robots.txt files; it is generally used to prevent a search engine from indexing individual pages. Robots.txt files, on the other hand, will prevent search engines from indexing a whole site or section of a site.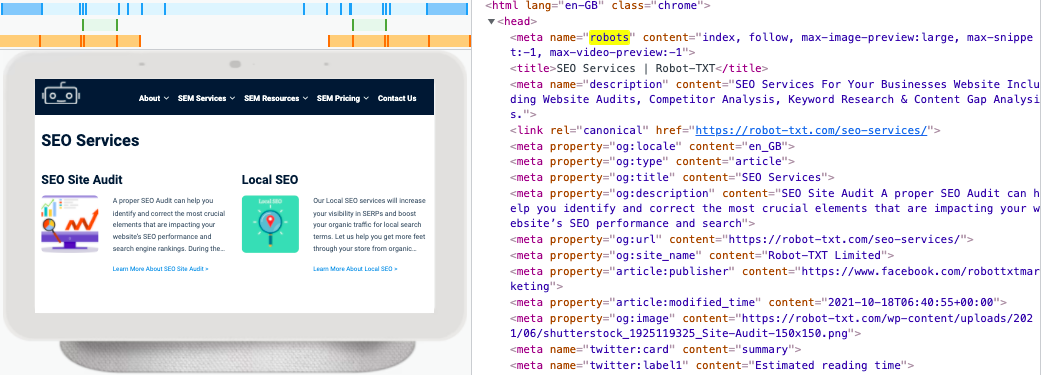
Conclusion
Metadata makes it easier for search engines to determine what your content is about, and how to display it in SERPs, and is therefore vital for SEO and SXO.
If you need help in optimising your metadata, so your website stands out in search results, we invite you to get in touch.
